探讨:二级指针删除链表节点
本文源自Linus Torvalds对一个问题的回答,以及网友的相关讨论。
关于如何删除链表中的一个节点,教科书式的做法是:
if (NULL != entry->prev)
{
entry->prev->next = entry->next;
}
else
{
list_head = entry->next;
}
free(entry);这里的特点是:①用到了双向链表 ②需要对头节点做特殊处理。
Linus对这种方法的评价是:
At the opposite end of the spectrum, I actually wish more people understood the really core low-level kind of coding. Not big, complex stuff like the lockless name lookup, but simply good use of pointers-to-pointers etc. For example, I’ve seen too many people who delete a singly-linked list entry by keeping track of the “prev” entry, and then to delete the entry…and whenever I see code like that, I just go “This person doesn’t understand pointers”. And it’s sadly quite common.
People who understand pointers just use a “pointer to the entry pointer”, and initialize that with the address of the list_head. And then as they traverse the list, they can remove the entry without using any conditionals, by just doing a “*pp = entry->next”.
Linus指出,更好的方法应该是通过一个二级指针来实现删除节点的功能,以消除对头节点的条件判断。例如:
void remove_if(node ** head, remove_fn rm)
{
for (node** curr = head; *curr; )
{
node * entry = *curr;
if (rm(entry))
{
*curr = entry->next;
free(entry);
}
else
curr = &entry->next;
}
}乍一看可能比较难懂,不妨通过一张图来看看。这是一个常见的带头指针的单向链表。
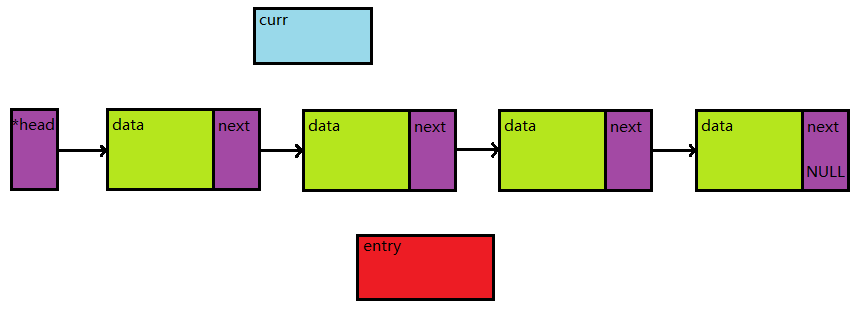
然后我们来运行代码,首先是 curr = head 和 entry = *curr。注意,左数第一个紫色块不是head,而是head解引用后的内容,此处的head参数实际上传入的是头指针的地址。
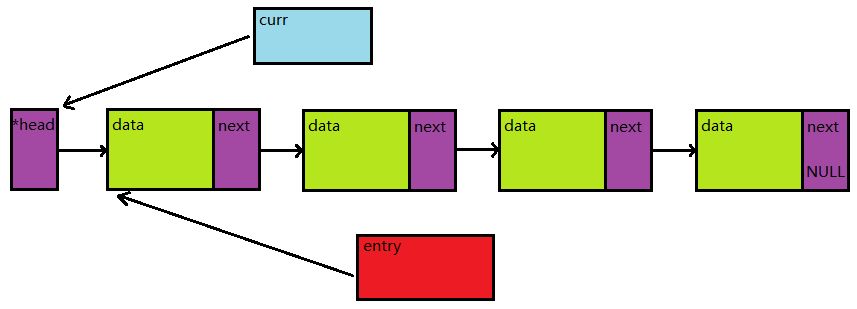
此时若删除节点,那么*head将指向下一个节点,并释放entry的空间:
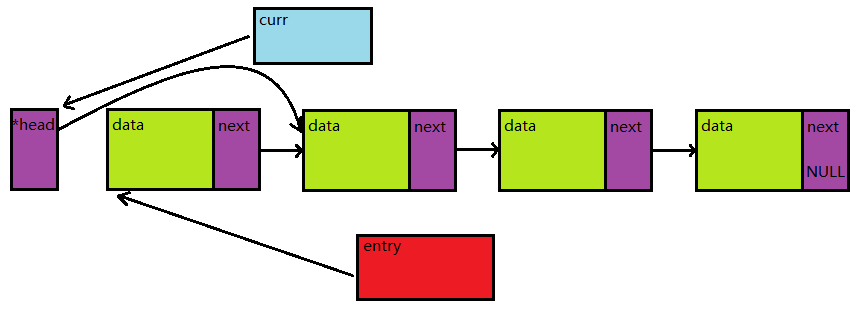
再来看看非头节点的情况,若运行到第二次循环,curr和entry的指向如下图:
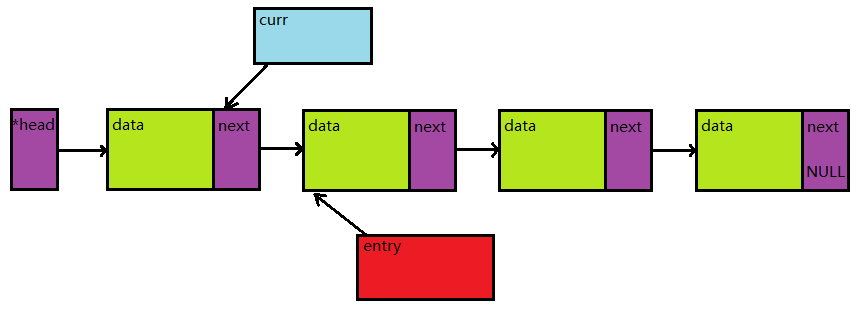
如果需要删除节点,那么:
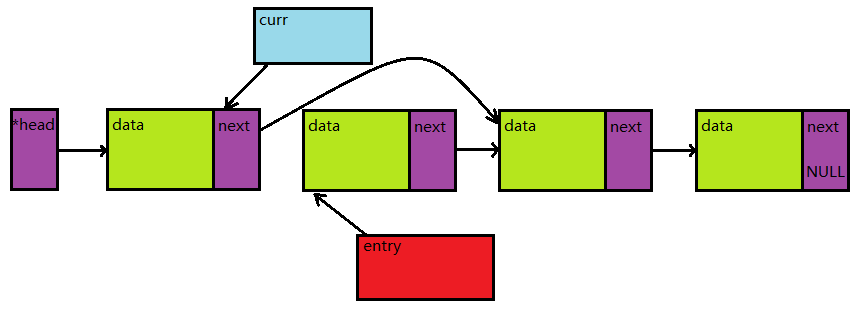
删除头节点和其他节点的操作完全是一致的,而且不需要引入prev域,对单向链表就可以进行操作。
暂且不考虑这种方法的运行效率如何,我们来分析一下两个原因:①为何处理头节点和其他节点的逻辑是一致的? ②为何不需要引入prev域?
一、从图中我们可以看到,*head和next域在实质上是等同的,所以通过二级指针curr可以无差别地访问头指针和节点的next域。或者,换一个角度思考,*head实际上是一个没有数据域的dummy node,这样理解的话,所谓的“头节点”也就不存在了,只有普通节点。
二、教科书式方法需要prev域的原因是,需要找到当前节点的前驱的next域,以改变其后继。从这里我们可以看到,删除链表节点的本质是改变前驱的next指针域。而改变next指针域并不需要对象的地址,只需要获取next指针域的地址即可,在这里,我们通过二级指针curr来保存next域的地址,达到修改前驱的next域的目的。同样,换一个思路来看,curr实际上保存的是当前节点的前驱的位置,在遍历链表时,curr与entry同步遍历,相当于同时保存了一前一后的两个节点位置,因此不需要prev域。
References
http://coolshell.cn/articles/8990.html
Linus Torvalds Answers Your Questions
Post Info
- Copyright Notice: Creative Commons BY-NC-ND 3.0